Appendicitis Operation
What is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch connected to the large intestine.
It can cause severe abdominal pain and requires prompt medical attention.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of appendicitis include:
- Sudden pain around the abdomen, often starting near the navel and shifting to the lower right side
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Abdominal swelling
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests to check for infection
- Imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan
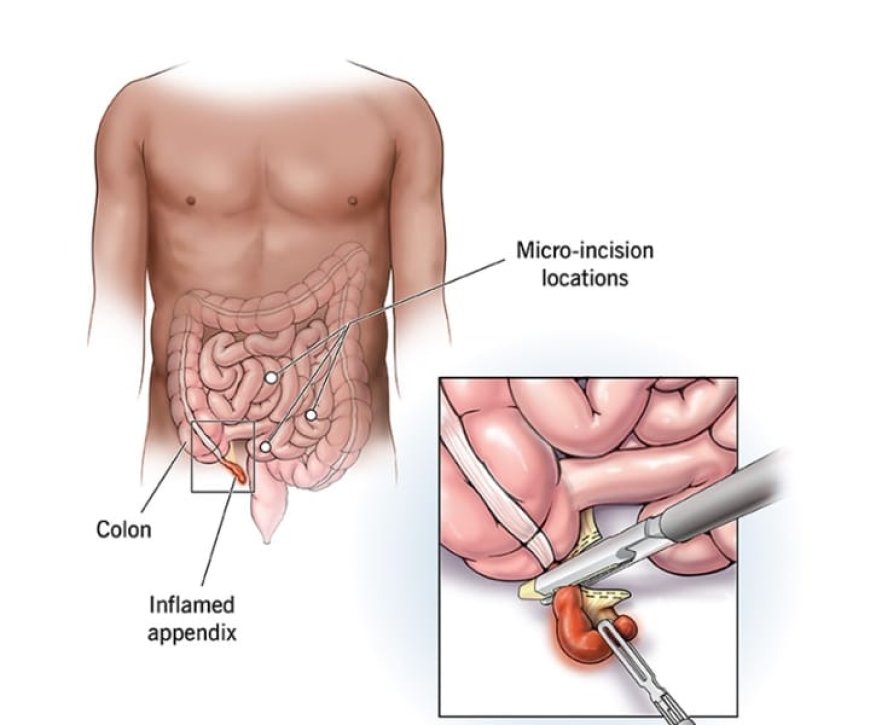
Surgical Procedure
The standard treatment for appendicitis is an appendectomy, which can be performed in two ways:
1. Open Appendectomy:
- A larger incision is made in the lower right abdomen.
- The appendix is removed through this incision.
2. Laparoscopic Appendectomy:
- Several small incisions are made in the abdomen.
- A camera and special instruments are used to remove the appendix, resulting in less pain and quicker recovery.
Recovery
- Hospital stay may range from a few hours to a couple of days, depending on the procedure and individual recovery.
- Most patients can resume normal activities within 1 to 3 weeks after surgery.
Risks
While appendectomy is generally safe, potential risks include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Injury to surrounding organs
Early diagnosis and treatment of appendicitis are crucial to prevent complications. If you experience symptoms of appendicitis, seek medical attention promptly.
What's Your Reaction?