What Are Genital Warts?
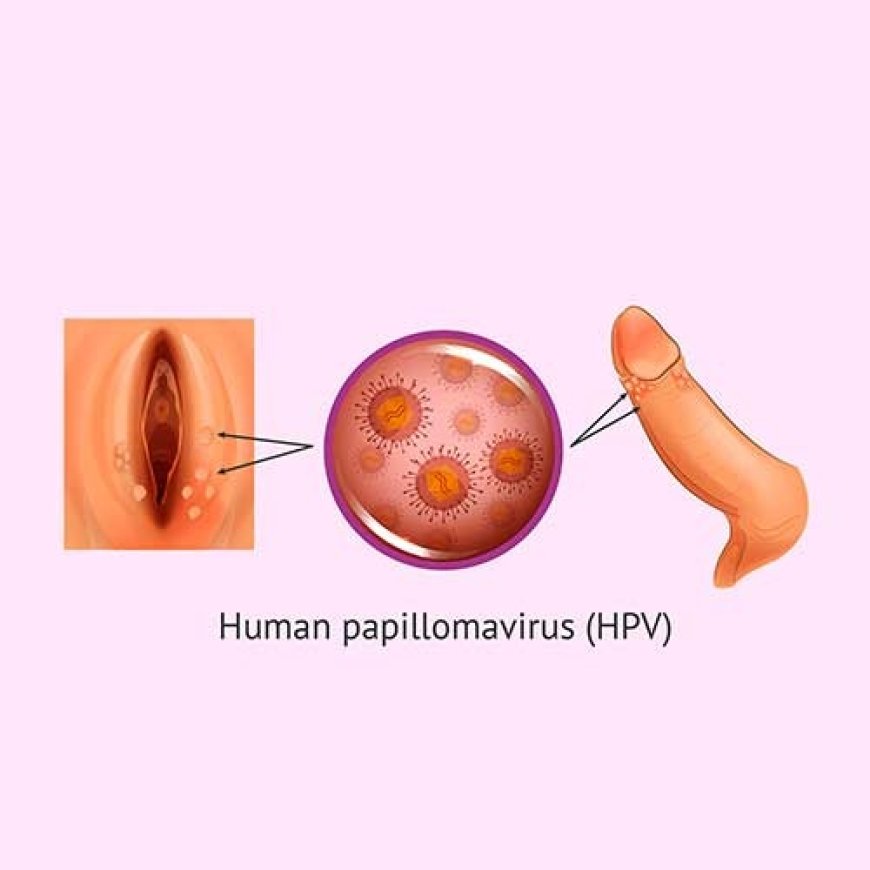
Genital warts are small growths or lumps that appear on the genital area, including the vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, and anus.
They are caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Causes
HPV Infection: Genital warts are primarily caused by low-risk strains of HPV, particularly types 6 and 11. These strains do not typically lead to cancer but can cause warts.
-Transmission: The virus is spread through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. It is possible to transmit the virus even when warts are not visible.
Symptoms
Appearance: Genital warts can be small, flesh-colored, or gray and may appear as single or multiple growths. They can have a cauliflower-like appearance.
-Location:They can develop on the genital area, inner thighs, or around the anus. In some cases, warts may also appear in the mouth or throat.
Discomfort: While genital warts are often painless, they can cause itching, irritation, or discomfort.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically made through a physical examination by a healthcare provider. In some cases, a Pap test may be performed for women to check for changes in the cervix associated with HPV.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for HPV itself, treatments are available to remove genital warts:
1. Topical Treatments: Prescription creams or solutions (e.g., imiquimod, podophyllin) can be applied directly to the warts to help remove them.
2. Cryotherapy: This involves freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen to destroy the tissue.
3. Electrosurgery: Warts can be burned off using electrical currents.
4. Surgical Removal: In some cases, warts may need to be surgically excised.
5. Laser Treatment: This approach uses laser light to remove warts, particularly in cases where other treatments have failed.
Prevention
Vaccination: The HPV vaccine (Gardasil) can protect against the most common cancer-causing strains of HPV and those that cause genital warts. It is recommended for preteens, but can be given up to age 26 (and in some cases, up to age 45).
Safe Sex Practices: Using condoms can reduce the risk of transmission, although they do not provide complete protection since HPV can infect areas not covered by a condom.
Regular Screenings: Routine Pap tests and HPV tests for women can help detect changes in cervical cells early.
What's Your Reaction?