Hepatitis B ----- A Sexually Transmitted Disease
Hepatitis B ----- A Sexually Transmitted Disease
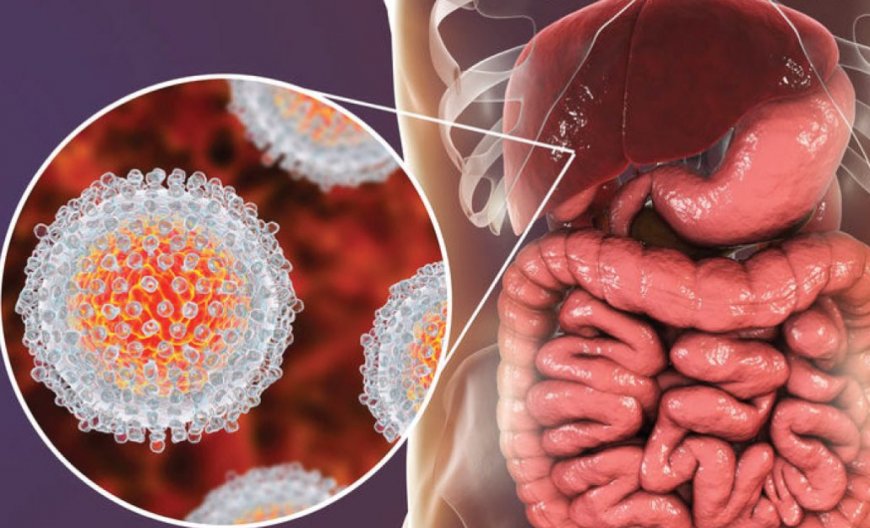
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects the liver and can lead to both acute and chronic diseases. It is primarily transmitted through contact with infectious body fluids, making it a sexually transmitted disease (STD).
*Transmission
Hepatitis B is transmitted through:*
- *Sexual Contact*: The virus can be spread through unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person.
- *Blood Contact*: Sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia, as well as exposure to infected blood.
- *Mother to Child*: An infected mother can transmit the virus to her baby during childbirth.
Symptoms
Many individuals with Hepatitis B may not show symptoms initially. However, when symptoms do occur, they can include:
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark urine
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
Prevention
Preventing Hepatitis B involves several strategies:
- *Vaccination*: The Hepatitis B vaccine is highly effective and is recommended for all infants and at-risk adults.
- *Safe Sex Practices*: Using condoms can significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
- *Avoid Sharing Needles*: Individuals should never share needles or personal items that may have blood on them.
Treatment
While there is no cure for Hepatitis B, several treatments can help manage the infection:
- *Antiviral Medications*: These can help reduce the viral load and prevent liver damage.
- *Regular Monitoring*: Individuals with chronic Hepatitis B should have regular check-ups to monitor liver health.
What's Your Reaction?